Histogram and frequency polygon
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
If you’re looking for a way to visualize data in a clear and concise manner, a cumulative frequency histogram and polygon may be just what you need. Not only do these graphs allow you to see the distribution of your data, but they can also help you identify outliers and trends.
However, many people may find the process of drawing a cumulative frequency histogram and polygon overwhelming or confusing. Figuring out how to collect the data, create the table, and draw the graph can be intimidating, especially if you’re not familiar with the terminology.
If you’re struggling with how to draw a cumulative frequency histogram and polygon, don’t worry! In this article, we’ll break down the process step-by-step so you can create professional-looking graphs with confidence.
First, let’s answer the question: what is a cumulative frequency histogram and polygon? Essentially, this type of graph shows the number of observations that fall within certain intervals. The intervals are listed on the x-axis, while the frequency (or number of observations) is listed on the y-axis. A cumulative frequency histogram shows the sum of the frequencies up to a certain point, while a cumulative frequency polygon connects the midpoints of the tops of the bars on the histogram.
To draw a cumulative frequency histogram and polygon, follow these steps:
Step 1: Collect and organize your data
The first step is to collect your data and organize it into intervals. For example, if you’re tracking the number of hours slept per night, you could create intervals such as 0-2 hours, 2-4 hours, 4-6 hours, etc. Make sure the intervals are mutually exclusive, meaning that each observation falls into only one interval.
Step 2: Create a frequency table
Next, create a frequency table that lists the intervals and the number of observations that fall within each interval. Calculate the cumulative frequency by adding up the frequencies as you go down the table.
Step 3: Draw the histogram
Using the interval values and the corresponding frequencies, draw the histogram by creating bars that represent each interval. Make sure the width of each bar is equal to the size of the interval, and that the height of the bar corresponds to the frequency. Remember, a cumulative frequency histogram shows the sum of the frequencies up to a certain point.
Step 4: Draw the polygon
To draw the polygon, connect the midpoints of the tops of each bar on the histogram with straight lines. The last point on the polygon should connect to the top right corner of the graph.
Now that you know the steps to draw a cumulative frequency histogram and polygon, let’s summarize the process and some important keywords:
To create a cumulative frequency histogram and polygon, collect and organize your data, create a frequency table, draw the histogram by creating bars that represent each interval, and then draw the polygon by connecting the midpoints of the tops of each bar on the histogram. Keywords to remember include intervals, frequencies, cumulative frequency, histogram, and polygon.
Personal Experience
When I first learned about cumulative frequency histograms and polygons, I found the process to be daunting. However, once I broke down the steps and practiced on different sets of data, I quickly became more comfortable with the concept. Now, I use these graphs frequently to display data in a clear and concise way.
Tips for Drawing a Cumulative Frequency Histogram and Polygon
One tip for drawing a cumulative frequency histogram and polygon is to choose appropriate intervals. You want to make sure the intervals are the right size so that you don’t have too many or too few bars on the graph. Another tip is to label your axes properly, including the units for the x and y-axes. Finally, make sure to include a title for your graph that summarizes what the data is showing.
Historgram and Polygon Together
When drawing a cumulative frequency histogram and polygon together, it’s important to remember that the polygon is a visualization of the data that connects the midpoint of each bar. This can help you see the overall trend of the data more clearly. Additionally, the cumulative frequency histogram can help you identify any outliers or unusual patterns that may be hiding within the data.
Using Software to Create Cumulative Frequency Histograms and Polygons
If you’re not comfortable creating a cumulative frequency histogram and polygon by hand, there are several software programs that can help. Microsoft Excel, for example, has a built-in histogram chart that can generate a cumulative frequency histogram and polygon for you. Other programs, such as SPSS and R, have more advanced options for data visualization.
Question and Answer Section
Q: What is the purpose of a cumulative frequency histogram and polygon?
A: A cumulative frequency histogram and polygon allows you to visualize the distribution of your data in a clear and concise way. It can also help you identify outliers or unusual patterns in the data.
Q: Why is it important to choose appropriate intervals when creating a cumulative frequency histogram?
A: Choosing appropriate intervals is important because you want to make sure that you have enough bars to show the distribution of the data without having too many that the graph becomes cluttered. Additionally, you want to make sure that each observation falls into only one interval.
Q: What is the difference between a cumulative frequency histogram and a frequency histogram?
A: A frequency histogram shows the number of observations that fall into each interval, while a cumulative frequency histogram shows the sum of the frequencies up to a certain point. A cumulative frequency polygon connects the midpoints of the tops of each bar on the histogram.
Q: How can software programs help with creating cumulative frequency histograms and polygons?
A: Software programs such as Microsoft Excel, SPSS, and R have built-in functions that can generate histograms and polygons for you based on your data. This can save time and make it easier to spot patterns or outliers within your data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, drawing a cumulative frequency histogram and polygon may seem overwhelming at first, but breaking down the process into steps can make it more approachable. Remember to collect and organize your data into intervals, create a frequency table, draw the histogram by creating bars and polygon by connecting the midpoints of each bar. Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can use software programs or other tools to make the process even easier. Whether you’re a student, a researcher, or just someone who wants to visualize data clearly, a cumulative frequency histogram and polygon can be a valuable tool in your toolkit.
Gallery
Histogram And Frequency Polygon - YouTube
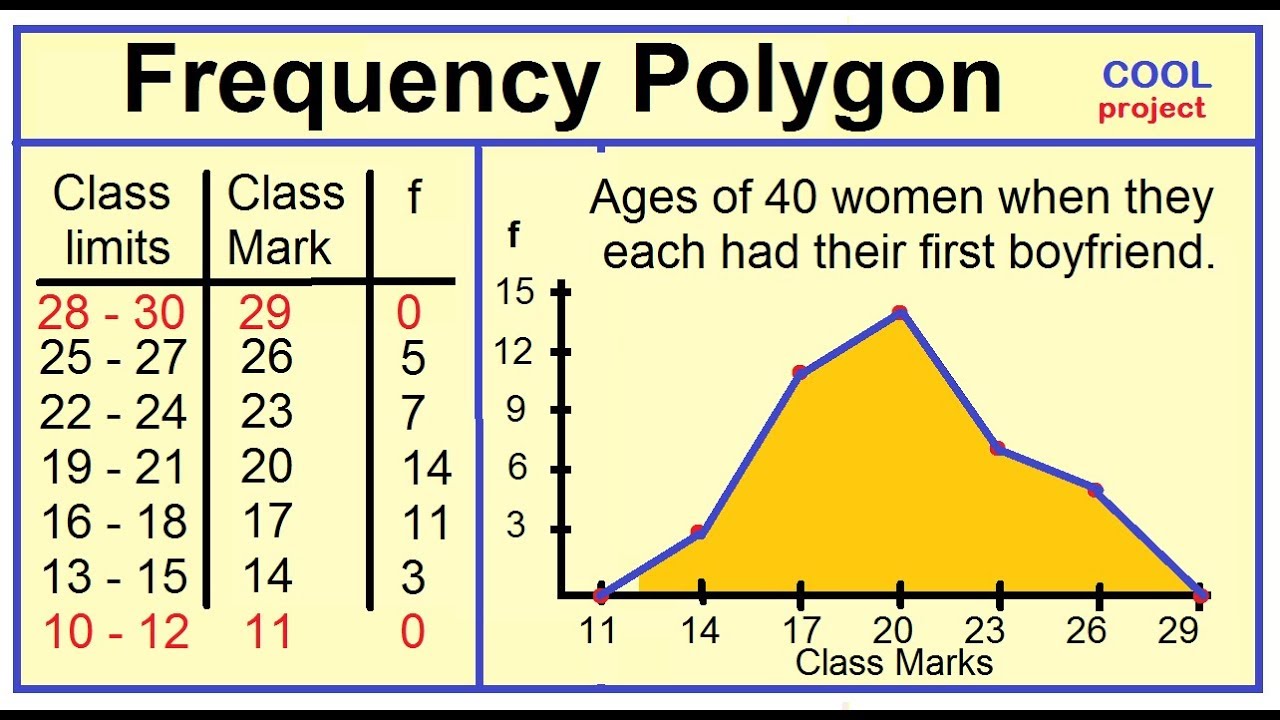
Photo Credit by: bing.com / polygon frequency histogram
Drawing Cumulative Frequency Histogram Polygon
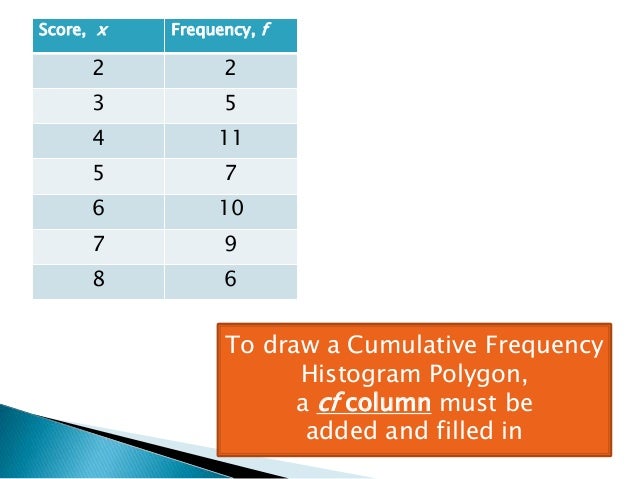
Photo Credit by: bing.com / cumulative histogram polygon
Basic Biostatistics - U1-L18 : Histogram And Frequency Polygon - YouTube

Photo Credit by: bing.com / polygon frequency histogram u1 biostatistics
Statistics Frequency Polygons: TutorTeddy.com

Photo Credit by: bing.com / frequency histogram polygon polygons statistics cumulative drawn over help various maths grade statistical thus provided use note kullabs
How To Draw A Histogram From A Frequency Table
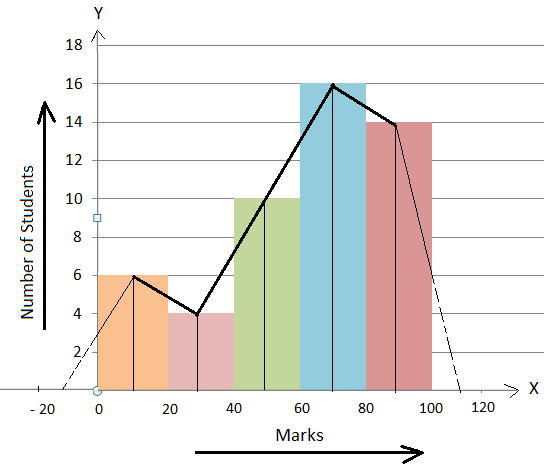
Photo Credit by: bing.com / histogram frequency polygon draw help method table math distribution examples constructing histograms steps





